Thermal shock testing is an important tool in environmental testing, providing essential insights into the durability of materials and components under extreme temperature conditions. By exposing a test subject to rapid changes between hot and cold temperatures, thermal shock testing helps engineers determine how well the material or component can withstand fluctuations in its environment. This type of testing yields valuable data that can be used to improve production processes, extend product life cycles and reduce operational costs. This article, will explore the benefits of thermal shock testing for environmental applications and discuss why it\’s such an effective method for evaluating materials\’ performance in challenging environments.
Improved Durability of Components Under Testing
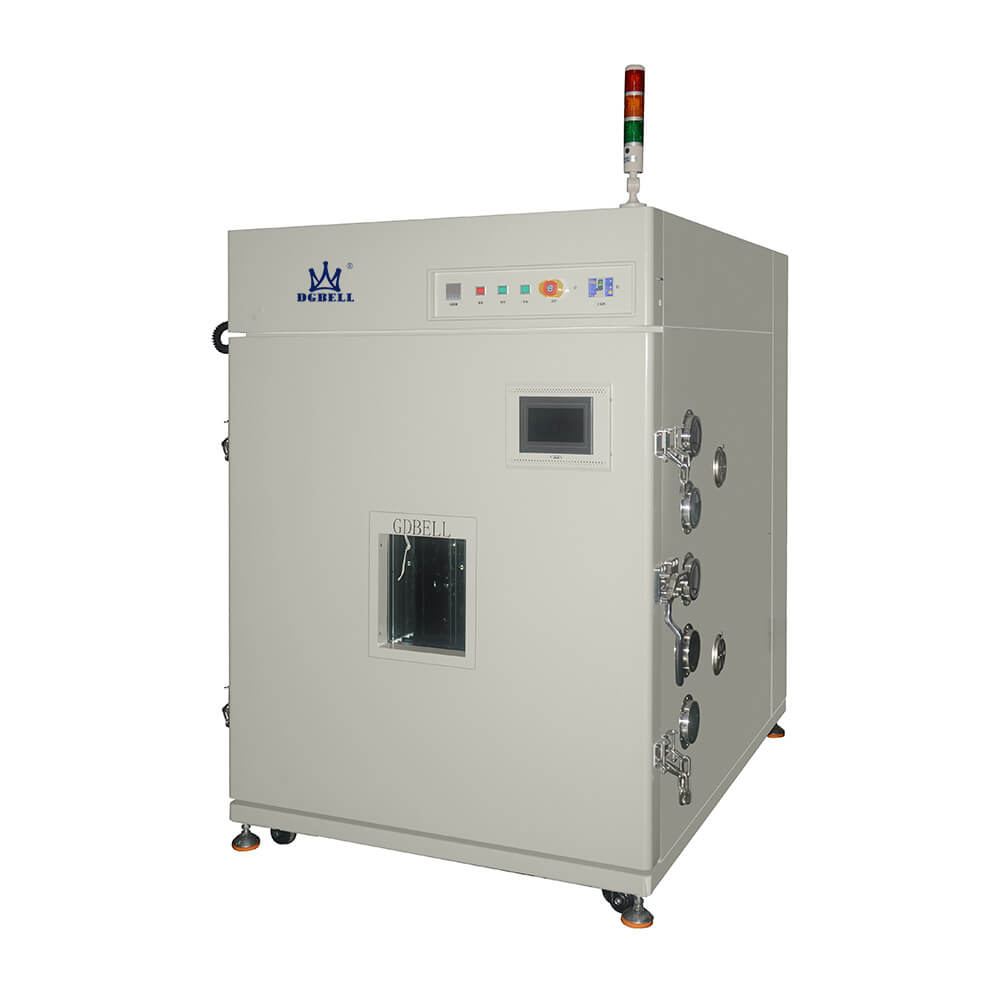 Thermal shock testing offers numerous benefits to environmental testing, one of which is the improved durability of components under test. This technique uses repeated and rapid temperature cycles to subject products and materials to extreme environmental conditions that they may face in real-world usage scenarios. As a result, thermal shock testing can identify weaknesses or vulnerabilities in components that could lead to failure when placed in an actual environment. By pushing these parts beyond their limits during the tests, engineers can determine how much stress any component can endure before breaking down. The increased durability provided by this type of assessment gives manufacturers more confidence in the products they produce, as well as a better understanding of what types of abuse their items may experience over time. Thermal shock testing also provides valuable insights into how certain materials behave under different temperatures and climates, giving designers even greater control over product outcomes during production processes.
Thermal shock testing offers numerous benefits to environmental testing, one of which is the improved durability of components under test. This technique uses repeated and rapid temperature cycles to subject products and materials to extreme environmental conditions that they may face in real-world usage scenarios. As a result, thermal shock testing can identify weaknesses or vulnerabilities in components that could lead to failure when placed in an actual environment. By pushing these parts beyond their limits during the tests, engineers can determine how much stress any component can endure before breaking down. The increased durability provided by this type of assessment gives manufacturers more confidence in the products they produce, as well as a better understanding of what types of abuse their items may experience over time. Thermal shock testing also provides valuable insights into how certain materials behave under different temperatures and climates, giving designers even greater control over product outcomes during production processes.
Reduced Risk of Product Failure During Environmental Changes
Thermal shock testing is an invaluable tool for environmental testing, as it can help reduce the risk of product failure due to changing temperatures. By exposing a product to extreme changes in temperature, manufacturers can identify potential weaknesses and areas of vulnerability before the final product is released into the market. This type of testing ensures that products will be able to withstand sudden shifts in their environment without failing or malfunctioning, ensuring greater customer satisfaction and increasing confidence in their performance. Thermal shock tests also allow manufacturers to make necessary upgrades or adjustments if needed; allowing them to create more reliable products with fewer chances of failure during operation. In short, thermal shock testing offers manufacturers a cost-effective solution for reducing the risk of product failure under varying environmental conditions.
Simulated Real-World Conditions for Engineering Evaluations
 Thermal shock testing is an important tool for environmental testing, providing engineering evaluations with simulated real-world conditions. This type of evaluation helps to identify how a product or system will react when exposed to rapid changes in temperature and humidity. Thermal shock tests can be used as part of a range of environmental assessments, including stress aging, corrosion resistance, and accelerated life cycle tests. By simulating the effects of extreme temperatures and other environmental variables on materials or components, engineers can develop solutions that are better prepared for long-term use in harsh environments. As such, thermal shock testing offers numerous advantages over traditional methods which cannot replicate these types of conditions.
Thermal shock testing is an important tool for environmental testing, providing engineering evaluations with simulated real-world conditions. This type of evaluation helps to identify how a product or system will react when exposed to rapid changes in temperature and humidity. Thermal shock tests can be used as part of a range of environmental assessments, including stress aging, corrosion resistance, and accelerated life cycle tests. By simulating the effects of extreme temperatures and other environmental variables on materials or components, engineers can develop solutions that are better prepared for long-term use in harsh environments. As such, thermal shock testing offers numerous advantages over traditional methods which cannot replicate these types of conditions.
Enhanced Efficiency in Production Testing
Thermal shock testing is a process used in environmental testing to improve the efficiency of production and product testing. Through this process, a variety of tests are conducted in rapid succession on products, often at extreme temperatures and other environmental conditions. By doing so, manufacturers can quickly assess the performance of their products under various conditions and make necessary changes or adjustments accordingly. This type of testing helps ensure that all components comply with quality standards and regulations while saving time for both production teams and customers alike. With thermal shock testing, companies can save money on product development costs by identifying any potential issues early on instead of waiting until later stages when they may be too costly to fix. Additionally, it ensures better safety protocols are taken into account during the manufacturing process as well as improved customer satisfaction due to faster delivery times and higher-quality results.
Conclusion
 Thermal shock testing is an essential part of environmental testing, providing valuable data on the ability of a material or device to withstand extreme temperature changes. When used as part of regular maintenance and quality assurance practices, thermal shock testing has been shown to improve material integrity and reliability across a range of products. By simulating real-world conditions in the lab, engineers can use these tests to identify potential weaknesses before they become serious issues in production. As such, thermal shock testing provides numerous benefits for improving product performance and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Thermal shock testing is an essential part of environmental testing, providing valuable data on the ability of a material or device to withstand extreme temperature changes. When used as part of regular maintenance and quality assurance practices, thermal shock testing has been shown to improve material integrity and reliability across a range of products. By simulating real-world conditions in the lab, engineers can use these tests to identify potential weaknesses before they become serious issues in production. As such, thermal shock testing provides numerous benefits for improving product performance and ensuring customer satisfaction.